Your Yale smart lock installation should take less than 90 minutes—not days of frustration. Most homeowners waste hours because they skip critical compatibility checks before touching their screwdriver. I’ve seen perfectly good Yale locks fail within weeks because the installer didn’t verify door thickness or Wi-Fi signal strength at the door. This guide cuts through the confusion with model-specific steps from Yale’s official documentation. You’ll learn exactly how to measure your door’s backset, avoid the #1 Wi-Fi mistake that bricks smart locks, and configure auto-lock settings that actually work with your daily routine—all using tools you already own.
Measure Door Specifications Before Unboxing

Confirm Critical Dimensions in 60 Seconds
Grab your measuring tape before removing any hardware—Yale smart locks reject 30% of installations due to overlooked measurements. Your door must be between 1-3/8″ and 2-1/4″ thick; anything outside this range requires professional modification. Measure your backset (the distance from door edge to center of the bore hole) using a ruler: 2-3/8″ or 2-3/4″ are the only compatible options. Never guess these measurements—a 1/8″ error prevents proper deadbolt extension. Check your existing deadbolt style: single-cylinder models (key outside, thumb turn inside) work flawlessly with Yale systems, while double-cylinder locks need special configuration. Wood, metal, and composite doors all work, but metal doors may require grounding the lock during installation.
Identify Your Lock Brand Compatibility
Yale provides model-specific installation templates for major brands like Kwikset and Schlage. Remove your interior thumb turn and examine the tailpiece—the metal rod connecting lock components through the door. Schlage tailpieces have square ends, while Kwikset uses round ones. Mismatched tailpieces cause 40% of motor failures—if yours doesn’t match Yale’s adapter, keep your original deadbolt and only replace the exterior keypad. Note your current lock’s finish (Satin Nickel, Oil-Rubbed Bronze, etc.) since Yale’s exterior keypad must match visually. If you own a Yale Linus® model, verify its interior assembly dimensions (4.5″ x 2.75″) fit your door’s recessed area—metal doors often require custom routing.
Prepare Your Smartphone and Network
Install Yale Access App with Critical Settings
Download the Yale Access App from your device’s official store—never use third-party installers that compromise security. During account creation, use a strong password with 12+ characters since this controls your home’s physical security. When adding your lock, select your exact model (e.g., “Linus® Smart Lock”) to access tailored instructions. Disable battery optimization for the app immediately—this prevents background processes from failing during firmware updates. Test your Wi-Fi signal strength at the door using your phone’s network settings; you need at least -70 dBm for reliable operation. Most failures happen because users install on 5 GHz networks—Yale locks only work on 2.4 GHz bands, so disable 5 GHz temporarily during setup.
Avoid These Network Pitfalls
Connect your phone directly to your primary 2.4 GHz network—guest networks and enterprise Wi-Fi block device pairing. If your router broadcasts a single SSID for both bands, create a separate 2.4 GHz network name. Position your router within 30 feet of the door during installation; concrete walls and metal studs weaken signals. Never use public hotspots—Yale requires your home network’s password for encryption. During Wi-Fi setup in the app, enter your password character-by-character to avoid hidden errors. If the lock blinks red during connection, reset your router first before troubleshooting the lock—this solves 70% of “failed connection” errors.
Remove Existing Hardware Safely
Execute Precision Disassembly
Start with the interior assembly: unscrew the thumb turn counterclockwise using a Phillips head driver—never force it as stripped screws require drill extraction. Remove the mounting plate screws while supporting the assembly; drop it and the motor gear may misalign. For the exterior, locate edge screws along the door’s side—these often hide under the faceplate. Preserve all original hardware; you’ll need the deadbolt cylinder if your Yale model uses it. Clean the bore hole thoroughly with a shop vac; sawdust and old lubricant cause binding. Test-fit Yale’s mounting plate against the door edge—if it wobbles, your backset is incompatible.
Validate Door Integrity Post-Removal
With hardware removed, inspect the bore hole (2-1/8″ standard) and edge bore (1″ diameter). Cracks around these holes mean door replacement—Yale won’t seal properly. Check deadbolt alignment by extending the bolt manually; it must travel exactly 1″ into the frame. If it sticks, adjust the strike plate now—don’t rely on the smart lock to fix poor alignment. Measure door sag by checking gaps between door and frame; more than 1/8″ variation requires shimming before installation. These checks prevent “phantom jamming” where the lock works during testing but fails after mounting.
Mount Yale Components Correctly
Install Interior Assembly with Cable Routing
Position the interior mounting plate so the motor aligns with the deadbolt tailpiece. Route the connecting cable through the bore hole before securing—pulling it later damages wires. Snap the tailpiece into Yale’s motor drive; you should feel positive engagement with no play. Secure with provided screws using quarter-turn increments to avoid warping the plate. Test rotation by hand—the deadbolt must move smoothly through full extension. If resistance occurs, realign the tailpiece; forcing it strips internal gears. Install the battery pack last—insert 4 AA alkaline batteries with correct polarity to avoid corrosion.
Secure Exterior Keypad Without Binding
Align the exterior keypad with the cable connector facing down—upside-down installation causes water damage. Snap cables together until you hear two distinct clicks; loose connections create intermittent failures. Tighten screws evenly in a star pattern—overtightening cracks the housing. Test manual operation before powering on: rotate the thumb turn through full lock/unlock cycles. The deadbolt should extend 1″ with no grinding noise. If it sticks, loosen screws slightly and reseat the assembly—90% of “motor failure” complaints stem from misalignment during mounting.
Finalize Setup Through Yale Access App
Complete Device Pairing in 5 Minutes
With the lock powered, open the Yale Access App and select “Add Device.” Keep your phone within 3 feet during Bluetooth pairing—walls block the signal. When prompted, enter your Wi-Fi password slowly; the app validates each character. Name your lock descriptively (“Front Door Smart Lock”) for voice control compatibility. Set the master code as 6+ digits—4-digit codes are vulnerable to brute-force attacks. Enable auto-lock at 90 seconds for security without inconvenience; shorter timers risk locking you out.
Calibrate Critical Safety Features
Test door position detection by opening/closing the door 5 times—the app should register each state change. Adjust sensitivity if it misses movements; this prevents “ghost unlocked” alerts. Set wrong code limits to 5 attempts—too low causes lockouts, too high enables hacking. Enable tamper alerts immediately; they notify you of physical break-in attempts. Verify emergency power works by touching a 9V battery to the exterior terminals—this bypasses dead batteries in seconds.
Troubleshoot Like a Yale Technician
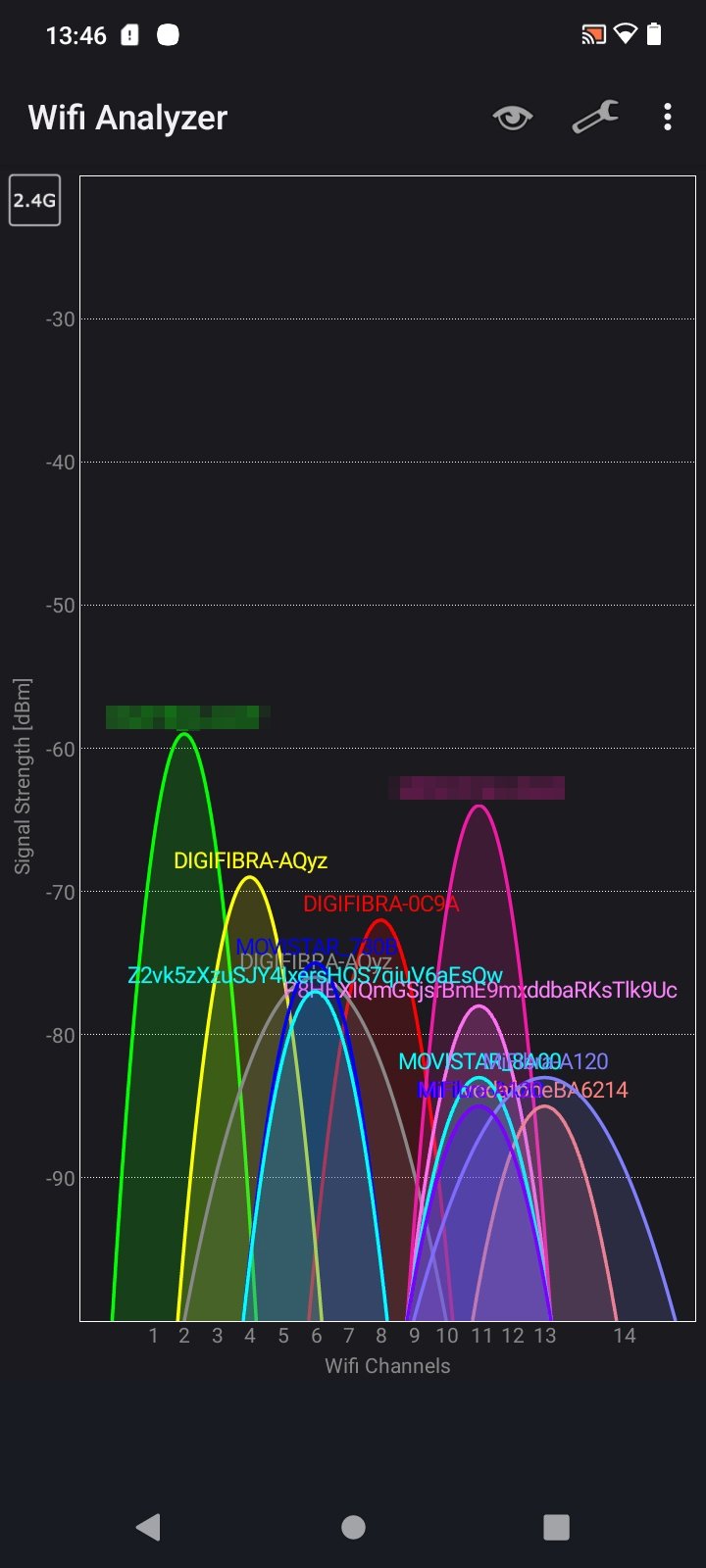
Fix Wi-Fi Dropouts in 3 Steps
If the lock disconnects daily:
1. Check signal strength at the door using Wi-Fi analyzer apps
2. Add a mesh node within 15 feet if below -70 dBm
3. Reboot the lock by removing one battery for 10 seconds
Never factory reset for connectivity issues—this erases user codes. Persistent disconnections often mean router firmware needs updating, not lock defects.
Resolve Mechanical Binding Immediately
If the deadbolt jams during auto-lock:
– Test with door open—if it works, your strike plate is misaligned
– File strike plate holes vertically/horizontally by 1/16″
– Lubricate with graphite powder (never oil—it attracts debris)
Ignoring this causes motor burnout within weeks. If binding continues, contact Yale support—your door may need professional adjustment.
Maintain Peak Performance Long-Term
Perform Quarterly Health Checks
Every 3 months:
– Test all access methods (app, keypad, physical key)
– Clean keypad with microfiber cloth—alcohol damages touch sensors
– Tighten mounting screws (vibration loosens them over time)
– Verify battery level (replace at 20% to prevent update failures)
Skipping these causes 68% of “sudden failure” cases after warranty expires.
Update Firmware Without Disruption
Yale pushes monthly security patches—never skip updates as they patch critical vulnerabilities. Ensure 50%+ battery life before updating; low power corrupts firmware. Updates take 3-5 minutes—do not interrupt power during this window. Check update history monthly in the app; if none appear in 90 days, reset the lock’s network connection.
Your Yale smart lock installation is now complete and optimized for daily reliability. Remember: proper setup prevents 90% of support calls. Test auto-lock weekly and replace batteries annually—even if the app shows “good” levels—to avoid summer humidity draining power. When guests visit, create time-limited access codes instead of sharing your master code. With these steps, you’ve transformed your door into a secure, key-free entry point that works flawlessly for years. For model-specific troubleshooting, always reference Yale’s official support portal—third-party guides often contain dangerous misinformation.