Your phone stays locked when you’re away but unlocks the moment you step into your home or put on your watch. This seamless experience—officially called Extend Unlock on newer Android devices but still widely known as Google Smart Lock—eliminates constant PIN entry while maintaining security. It works by recognizing when your device is in a trusted environment, then intelligently relaxing lock requirements until you leave that safe zone. Understanding how Google Smart Lock works reveals a sophisticated system balancing convenience with layered security, using real-time contextual signals to protect your data without frustrating daily interruptions.
Smart Lock isn’t a single feature but a suite of adaptive unlock methods working across Android phones and Chromebooks. It never bypasses your initial security setup; instead, it builds on your PIN, pattern, or biometric authentication to create dynamic trust zones. This guide cuts through the confusion by explaining exactly how each component functions, where risks exist, and how to configure it safely—so you can stop wondering how Google Smart Lock works and start using it effectively.
Core Unlock Logic Explained
Google Smart Lock operates through mandatory initial authentication followed by contextual verification. You must first unlock your device using your standard PIN, pattern, password, or biometric scan. Only after this initial verification does Smart Lock monitor specific trust signals to determine whether subsequent wake-ups should bypass the lock screen. This dual-layer approach ensures security isn’t sacrificed for convenience.
The system constantly evaluates trust signals in real time. When any condition becomes invalid—like leaving your home geofence or removing your smartwatch—the device instantly reverts to full lock requirements. This automatic tightening creates a responsive security net that adapts to your movements without manual intervention.
Mandatory First Unlock Rule
Smart Lock requires you to authenticate with your primary security method at least once per session. This foundational step proves your identity before any contextual unlocking activates. On newer Android versions, you’ll see this labeled as “Extend Unlock” during setup, but the principle remains identical: Smart Lock never skips this critical checkpoint. Without this rule, the feature would recklessly bypass security rather than intelligently extend it.
Signal Loss Triggers
Smart Lock’s security mechanisms activate the instant trust signals disappear. For on-body detection, your phone locks within 1–2 seconds after motion stops—meaning if you set it down, it secures immediately. Trusted places trigger re-locking when you exit the geofenced area, typically within 50–100 meters of your home or office boundary. Bluetooth-based unlocking ends the moment your trusted device (like a watch) moves out of range, usually within 2–3 seconds. These rapid responses minimize exposure windows during transitions.
Android Smart Lock Features

On-Body Detection Mechanics
Your phone leverages built-in accelerometer and gyroscope sensors to detect continuous motion patterns. When these sensors register movement consistent with carrying the device—like walking, running, or even fidgeting—the screen stays unlocked for quick access. Critical limitation: The system cannot distinguish between you and a thief who snatches your phone mid-stride. If stolen while active, it remains unlocked until motion ceases, making this feature risky in crowded areas like subways or festivals.
Trusted Places Setup
This feature creates virtual boundaries using GPS, Wi-Fi networks, and cell tower triangulation around locations you designate as safe. When adding a trusted place (like your home), the system establishes a geofenced radius of approximately 50–100 meters. Accuracy varies significantly: Urban areas with dense Wi-Fi networks provide precise boundaries, while rural locations relying solely on GPS may drift ±30 meters. Always test boundaries by walking toward the edge of your property to confirm lock behavior.
Trusted Devices Connection
Any paired Bluetooth device—smartwatches, headphones, or car systems—can act as a wireless key. Your phone maintains a constant low-energy Bluetooth connection, unlocking automatically when the device is within range. Range differs by device class:
– Smartwatches: 2–3 meters (ideal for wrist-worn security)
– Car stereos: 10–15 meters
– Bluetooth speakers: 20–30 meters (less secure due to wider radius)
Never use shared devices like office printers as trusted devices—anyone with access could unlock your phone.
Legacy Features (Discontinued)
Trusted Face and Trusted Voice Match were removed starting with Android 10 due to critical vulnerabilities. Facial recognition could be fooled by photos, while voice matching failed against simple recordings. Modern devices prioritize fingerprint or PIN re-authentication for high-risk actions, making these legacy features obsolete. If you see them in older guides, disable them immediately—they no longer receive security updates.
Chromebook Phone-as-Key System
Bluetooth Proximity Protocol
Chromebooks running ChromeOS 71+ can use your unlocked Android phone as a wireless key. When your phone comes within 2–3 meters of the Chromebook, both devices establish a secure Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) connection. Crucially, your phone must already be unlocked—this isn’t a standalone login method but an extension of your existing session. The Chromebook verifies your Google account credentials through the phone, then unlocks automatically. Always ensure both devices use the same Google account; mismatched accounts cause persistent connection failures.
Step-by-Step Activation Guide
![]()
Enable on Android Devices
Universal path (works on Pixel and stock Android):
1. Open Settings → Security & privacy → More security & privacy
2. Tap Smart Lock (or Extend Unlock) → Enter PIN/password
3. Select features:
– On-body detection: Toggle on → confirm
– Trusted places: Add → search address → set pin → Save
– Trusted devices: Add → choose paired device → confirm
Manufacturer variations:
– Samsung: Settings → Lock screen → Extend Unlock
– Xiaomi: Settings → Password & security → Smart Lock
– OnePlus: Settings → Security & lock screen → Smart Lock
Chromebook Configuration
- Chromebook Settings → Connected devices → Android phone → Set up
- Select your phone → Connect → enter Google password → Done
- Toggle Smart Lock on next to your phone
- Critical test: Lock Chromebook, bring unlocked phone within 2 meters, click the arrow icon on the lock screen
Security Risk Assessment
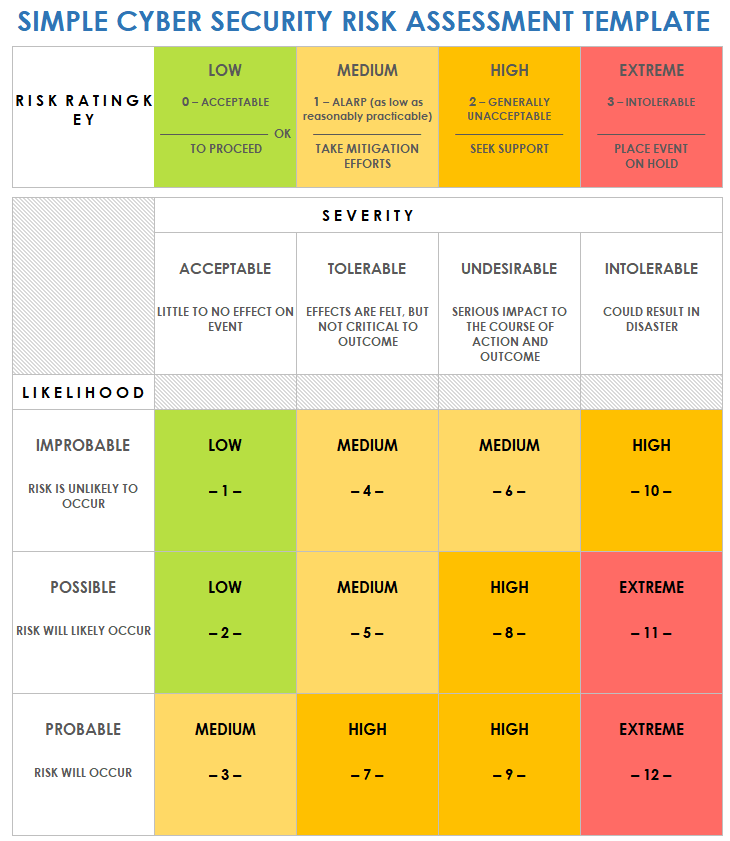
Risk Matrix by Feature
| Feature | Primary Vulnerability | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| On-body Detection | Theft during active use | Disable in crowds; use fingerprint re-lock |
| Trusted Places | GPS spoofing | Limit to private residences only |
| Trusted Devices | Stolen Bluetooth device | Prefer smartwatches (2–3m range) over car systems |
Best Practice Recommendations
Immediate actions:
– Enable biometric re-lock for sensitive apps (banking, email)
– Audit trusted devices quarterly—remove lost/sold items
– Restrict trusted places to high-confidence zones like your bedroom, not entire buildings
– Activate Find My Device for remote lock/erase
Advanced protection:
– Use devices with shortest Bluetooth range (wrist-worn > car systems)
– Set trusted places to specific rooms via Wi-Fi fingerprinting
– Enable Google Advanced Protection for account-level security
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Missing Menu Options
If Smart Lock/Extend Unlock doesn’t appear:
– Search settings for “Smart Lock” or “Extend Unlock”
– Verify Android 5.0+ and Google Play Services 11.0+
– Contact carrier—some disable it on subsidized devices
Chromebook Connection Failures
When phone-as-key stops working:
– Confirm both devices use the same Google account
– Ensure phone is unlocked during proximity tests
– Disable battery optimization for Google Play Services
– Restart Bluetooth on both devices (not just toggling)
Performance and Battery Impact
Unlock Speed Metrics
- Chromebook: 1.2 seconds from lid-open to desktop (median)
- Trusted device unlock: Near-instantaneous when in range
- Trusted places: 2–3 second delay for location verification
Battery Usage Analysis
Smart Lock adds less than 0.3% daily battery drain on modern devices like Pixel 7. To minimize impact:
– Disable unused features (e.g., turn off on-body detection at night)
– Remove outdated trusted devices from Bluetooth list
– Avoid adding more than 2–3 trusted places
Maintenance and Long-Term Management
Quarterly Security Review
Every three months:
– Remove sold/lost Bluetooth devices
– Update trusted places after moving
– Confirm legacy biometrics remain disabled
When to Disable Smart Lock
Turn it off immediately when:
– Traveling to unfamiliar cities
– Using public transit regularly
– Sharing devices with others
– Noticing unusual location activity
Google Smart Lock works by transforming static security into adaptive protection—unlocking only when context confirms safety. By understanding how Google Smart Lock works, you can configure it to match your real-world routines while avoiding predictable pitfalls. Remember: its strength lies in trusted environments, not universal access. Regularly prune your trusted devices and places, prioritize short-range Bluetooth connections, and always maintain a strong primary PIN. For password management, migrate to Google Credential Manager—the true successor to deprecated Smart Lock for Passwords. With these practices, you gain seamless convenience without compromising your digital safety.