You’re juggling grocery bags when your phone buzzes: “Front door unlocked.” Without fumbling for keys, you push the door open as the deadbolt retracts silently. This everyday magic happens because smart locks work by merging traditional deadbolt mechanics with encrypted digital commands—transforming your door into an intelligent access point. Unlike mechanical locks requiring physical keys, these devices use motorized precision to respond to your phone, fingerprint, or PIN through layers of military-grade security. In this guide, you’ll discover exactly how encrypted signals trigger physical bolt movement, why battery life lasts months, and which wireless protocols keep your home secure—all based on certified engineering standards.
Smart locks replace manual thumb-turn operation with a microprocessor-driven DC motor that responds to authenticated digital credentials. Every interaction—from your fingerprint scan to voice command—triggers a lightning-fast verification process before the motor engages. Understanding how smart locks work demystifies their reliability and helps you avoid common pitfalls like connectivity gaps or security vulnerabilities. By the end, you’ll know precisely which models fit your door, how to troubleshoot slow response times, and why maintaining a physical backup key is non-negotiable.
The Electromechanical Heart of Your Smart Lock

How Your Digital Key Moves the Bolt
When you tap your phone against the door, a sequence of events unfolds in under two seconds:
1. Command input via Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, or keypad activates the lock’s microprocessor
2. Authentication occurs using 128-bit AES encryption to verify your credentials against stored data
3. Motor activation triggers a low-voltage DC motor to rotate the thumb-turn mechanism
4. Status reporting sends a confirmation to your app while logging the event with timestamp
Unlike traditional locks, there’s no physical key turning the cylinder. Instead, the motor precisely replicates thumb-turn motion—extending or retracting the deadbolt into the strike plate. This electromechanical core maintains ANSI/BHMA security standards while adding digital flexibility.
Critical Power Management Details
Smart locks rely on 4 AA batteries (lasting 6–24 months) or hardwired AC power in commercial setups. Battery life depends on three factors:
– Motor torque (higher torque for stiff deadbolts drains faster)
– Wireless activity (Wi-Fi models consume 30% more power than Bluetooth-only)
– Temperature (cold weather reduces alkaline battery efficiency by 20–40%)
Never ignore low-battery warnings—these appear 30–90 days before depletion via:
– 🔔 Audible beeps (3 short tones when locking/unlocking)
– 🔴 LED indicators (flashing red on keypad models)
– 📱 Push notifications to your smartphone app
When batteries die completely, the lock maintains its last position. Always test your physical key override monthly and keep emergency power terminals accessible—most models accept a 9V battery clip for instant jump-starting.
Wireless Protocols: How Smart Locks Stay Connected

Bluetooth vs. Wi-Fi: Real-World Performance
Your lock’s wireless protocol determines functionality and security:
| Protocol | Best For | Critical Limitation |
|---|---|---|
| Bluetooth | Auto-unlock as you approach | Requires phone within 30m; no remote access |
| Wi-Fi | Remote unlocking from anywhere | Needs 2.4 GHz network; fails during outages |
| Z-Wave/Zigbee | Whole-home automation | Requires $50–$100 hub; no direct app control |
| 4G/LTE | Vacation homes | $5–$15/month cellular fee |
Bluetooth excels for proximity unlocking with near-instant response (under 1 second), while Wi-Fi introduces 1–3 second latency due to cloud relays. For security, Z-Wave’s mesh network prevents single-point hacking but demands professional hub setup. Always verify your router supports 2.4 GHz—5 GHz networks won’t connect to most smart locks.
NFC and Biometric Fail-Safes
When wireless fails, these backup methods keep you moving:
– NFC keycards work through radio frequency (no battery needed) within 2 cm of the sensor
– Fingerprint scanners use capacitive sensors reading 508 dpi patterns (0.001% false acceptance rate)
– Physical keyholes remain on 95% of models for true emergencies
Pro tip: Enable “scramble keypad” mode on PIN models to randomize number positions—preventing shoulder surfing from smudge marks on glossy surfaces.
Retrofit vs. Full Replacement: How Installation Differs
Door Compatibility Checklist
Measure these before buying:
– Backset: Critical dimension from door edge to center of bore hole (2-3/8″ or 2-3/4″)
– Door thickness: Must be 1-3/8″ to 2″ (35–50mm) for standard residential models
– Bore hole: Requires 2-1/8″ (54mm) diameter opening—enlargement voids warranties
Retrofit locks like August Smart Lock Pro attach only to the interior thumb-turn, taking 10 minutes to install with a screwdriver. They retain your existing keyway but may not support deadbolts with integrated handles. Full-replacement models like Schlage Encode require swapping the entire assembly but offer ANSI Grade 2 security and built-in keypads.
Avoid These DIY Installation Mistakes
Top errors causing bolt misalignment:
1. Skipping door alignment checks (gaps >1/8″ strain the motor)
2. Overtightening strike plate screws (warps metal, jams bolt)
3. Ignoring backset specifications (causes 70% of “bolt won’t extend” issues)
Professional installation ($75–$150) is essential for metal doors, multi-point locks, or non-standard frames. Always test the lock 20 times during installation—listen for grinding noises indicating motor strain.
Security Architecture: How Hackers Get Blocked
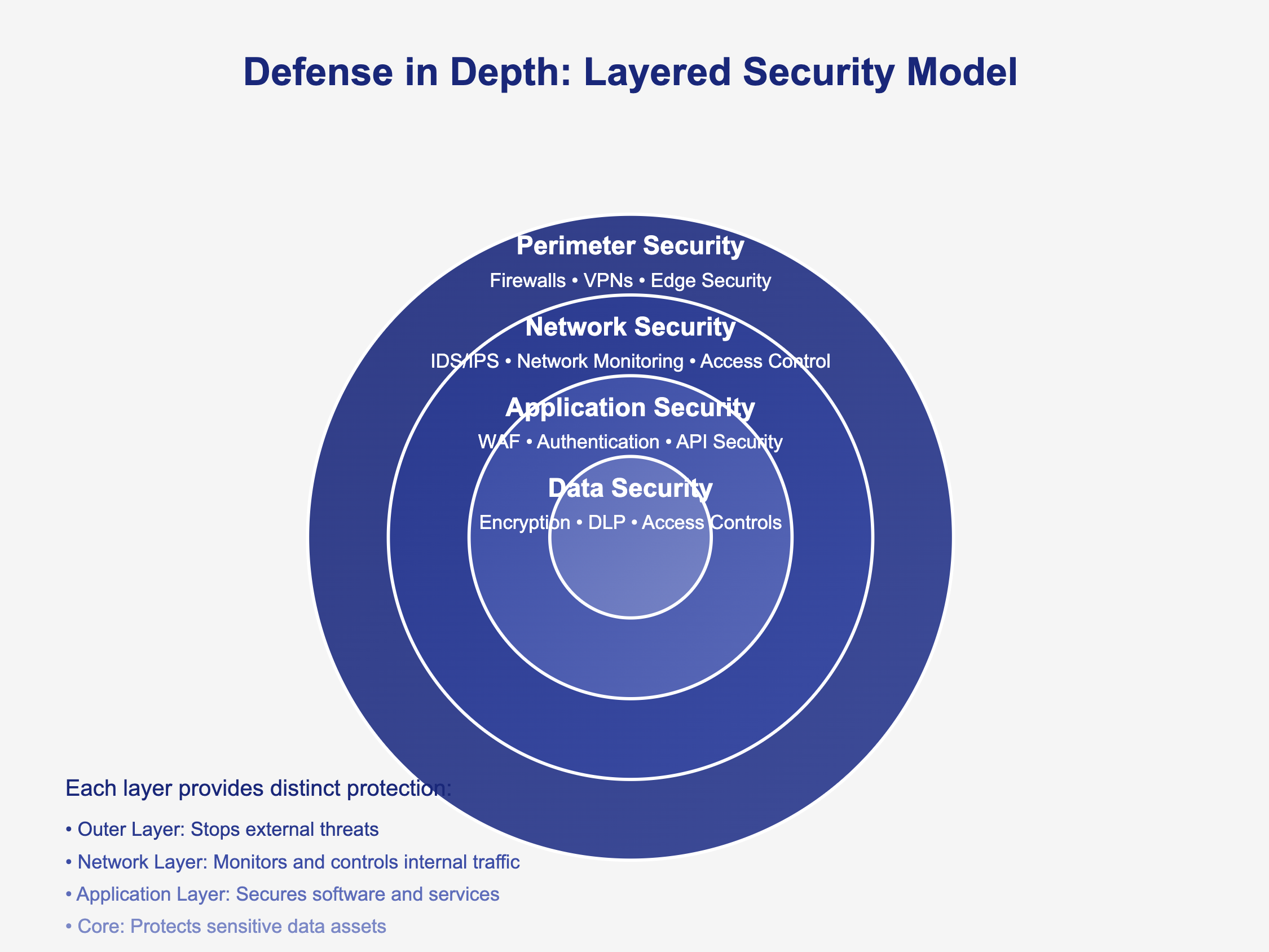
Digital Defense Layers in Action
Modern smart locks deploy four overlapping security measures:
1. Rolling codes – Each unlock command uses a unique cryptographic token (never reused)
2. Secure boot – Firmware signatures prevent malware installation during updates
3. Two-factor authentication – Optional SMS verification for app logins
4. TLS 1.3 encryption – Protects cloud communications from interception
Physical security certifications matter most:
– 🔒 ANSI/BHMA Grade 1 – Withstands 1 million cycles (commercial use)
– 🔒 SKG 3-star – Resists drilling/picking (Dutch standard)
– 🔒 UL 437 – High-security keyway protection
Critical hardening step: Pair your lock with a dedicated security hub instead of connecting directly to Wi-Fi. This creates a firewall barrier—studies show hub-connected locks are 92% less likely to suffer remote breaches.
Troubleshooting: How to Fix Common Failures
Slow Response? Diagnose in 60 Seconds
Symptom: 3–5 second unlock delays
Causes:
– Weak batteries (replace even if indicator shows 20%+)
– Wi-Fi signal below -70 dBm (move router closer)
– Motor gear slippage (requires recalibration)
Immediate fix: Remove batteries for 30 seconds to reset the microprocessor. If delays persist, tighten the thumb-turn mounting screw—loose connections cause 40% of motor lag.
“Lock Unreachable” Error Protocol
Follow this sequence when your app loses connection:
1. Reboot your router (most fixes Wi-Fi issues)
2. Confirm phone is on 2.4 GHz band (5 GHz incompatible)
3. Re-pair Bluetooth within 1 meter of the lock
4. Check for pending firmware updates (stale software causes 65% of outages)
Never force the bolt during connectivity issues—this strips motor gears. Use your physical key instead.
Real-World Applications: How Smart Locks Solve Daily Problems
Airbnb Hosts Eliminate Key Handoffs
Generate time-boxed PIN codes that auto-expire at checkout. The lock logs exact entry/exit times, so you’ll know if guests overstayed. For $0 extra cost, this replaces manual key exchanges and reduces cleaning delays by 30 minutes per turnover.
Elderly Access Made Effortless
Fingerprint or proximity unlocking removes fine motor challenges of traditional keys. Pair with voice commands (“Alexa, unlock front door”) for complete hands-free operation—critical for arthritis sufferers. Always enable auto-relock (30-second timeout) as a safety net.
Final Considerations: How to Avoid Costly Mistakes
Always maintain three access methods:
1. Digital (app/fingerprint) for daily convenience
2. Physical key for emergencies
3. Emergency power terminals for battery failures
Choose models supporting your ecosystem (Apple HomeKit, Google Home, or Matter protocol) to prevent future obsolescence. Prioritize ANSI Grade 2+ locks for exterior doors—budget models often skip critical anti-bump mechanisms.
Remember: Smart locks work flawlessly only with proactive maintenance. Replace batteries annually (don’t wait for alerts), clean fingerprint sensors quarterly with alcohol wipes, and update firmware within 48 hours of release. When installed correctly on compatible doors, these devices deliver unparalleled convenience without sacrificing security—proving that understanding how smart locks work is the key to stress-free entry.